What Is a MAC Address?
No matter how you connect to the Internet, it always takes a variety of software and hardware working together to allow communication from your device to other devices. Just like every home has a physical address, every network-connected device has a MAC address. These identifying addresses are required for a device to be on a network. In this article, learn what MAC addresses are and how to find yours on your device.
What is a MAC address?
A MAC, or Media Access Control, address identifies your physical device so that you can connect to a network. It is different from an IP address; unlike Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, the manufacturer assigns MAC addresses to devices at the factory.
Think of it as a sort of serial code or physical network address that identifies the device to the network. When every Internet-capable device begins in development, the manufacturer assigns each device's network adapter a unique address to identify it on network interfaces. This gives the device the ability to connect to a network, which is necessary for the device to connect to the Internet. Because the number is assigned to the physical device by the manufacturer, in most cases, it can't be changed by the user. Once again, the manufacturer defines the address and for most devices the end user cannot modify it. Sometimes, however, a MAC address can be cloned and assigned to an additional device.

Usually, they connect to a component in your device called a network interface controller (NIC). The NIC communicates your MAC to the network, enabling the connection.
What does a MAC address look like?
It is a 48-bit, 12-digit combination of numbers, letters, and colons. Here is a MAC address example:
00:00:5e:00:53:af
Also, each manufacturer has its own unique identifier within the address known as the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI). See some well-known manufacturers' OUIs below.
- Cisco: 00-40-96
- Nortel: 00-04-DC
- Dell: 00-14-22
The purpose of MAC in networking
The purpose of these MACs is to identify devices on a network. To prevent unauthorized access to a network, set the router to only accept devices specific to its network through MAC filtering. This way, even if the IP address changes, the router still identifies the device.
Additionally, the address is sometimes used in data recovery to connect to a device. Media Access Control addresses can be used to diagnose network problems because in most cases, the addresses never change. This makes it easy for network administrators to pinpoint problems with specific devices sending and receiving data on the network.
What is the difference between a MAC address and an IP address?
Though IPs and MACs may seem similar to those unfamiliar with networking, they’re quite separate. The two serve different purposes and function at different layers of the OSI model.
Essentially, an IP address is a logical address used for routing data across networks, and a MAC address is a physical address used for communication locally within a single network. IP addresses operate at the third layer of the OSI model, the network layer, while MAC addresses are used at the second layer, the data link layer.
Furthermore, IP addresses typically change; they’re assigned by your router or DHCP, and if you have a dynamic IP, it will change over time. MACs, however, do not change over the life of the device in most cases.
Types of MAC addresses
There are three types of Media Access Control addresses: unicast addresses, multicast addresses, and broadcast addresses.
Unicast addresses are assigned to a single network interface card (NIC). They direct data to one receiving device, and each device on a network has one. The address ensures that data packets sent over the network reach the correct destination device.
Multicast addresses allow a device to send a packet to a set of destinations. This helps in situations where data needs to go to multiple recipients at once, such as with video streaming. These addresses reduce traffic by ensuring that packets only go to devices with an explicit interest in seeing them.
Broadcast addresses target all network interface cards on a network or network section. They send data to all devices on the network and are used for network-wide announcements due to their efficiency.
Ultimately, each type of Media Access Control address serves a different purpose and has its own role in the flow of data across network systems.
How to find your MAC address
If you want to find out what is your MAC address, you can find it through the command prompt or through your computer's settings. Follow the instructions below to find your MAC on your computer or phone.
How to find your MAC address on Windows
To find your the address on Windows:
1. Open the command prompt.
2. Type ipconfig /all and press Enter.
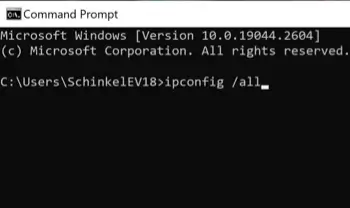
You’ll get a lot of information, including your MAC address next to the “Physical Address” label.
How to find your MAC address in MacOS
To find your address on a Mac:
1. Open the Apple menu.
2. Click System Settings and then Network.
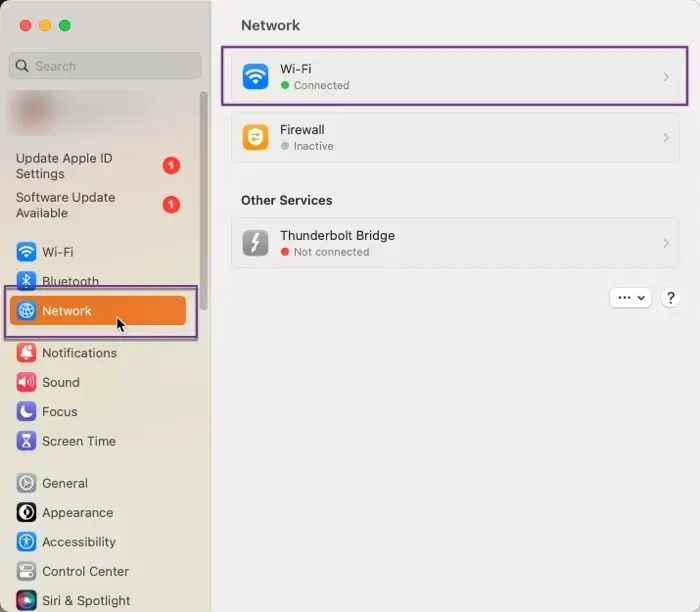
3. Select your network connection and click Advanced.
You’ll be able to see your MAC labeled as “WiFi MAC Address.”
How to find your MAC address on a Chromebook
To find the address on a Chromebook:
1. Sign into your Chromebook.
2. At the bottom right, select the time.
3. Select your WiFi network.
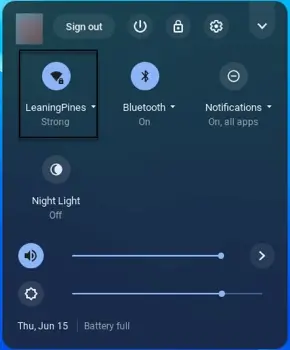
4. At the top of the box, select Information.
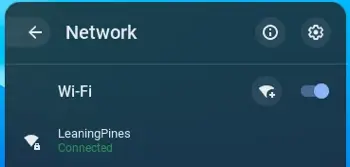
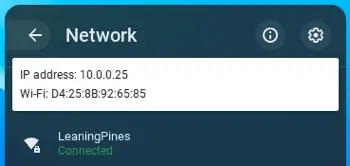
There, you’ll see the IP and MAC of your Chromebook with the MAC labeled “WiFi.”
How to find your iPhone MAC address
To find the address on an iPhone, iPad, or iPod:
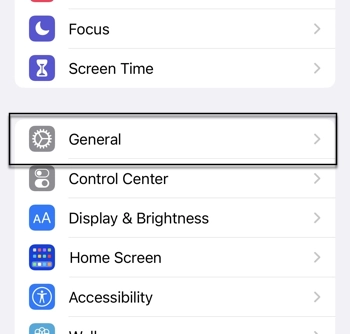
1. Open the Settings app.
2. Select General.
3. Select About.
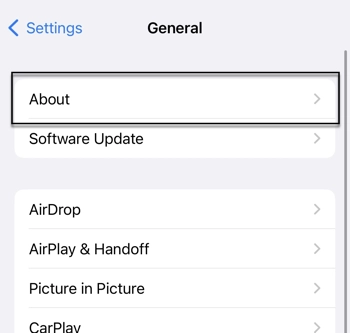
4. Scroll down until you see WiFi Address.
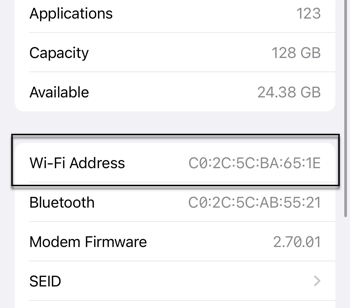
The WiFi address is your MAC.
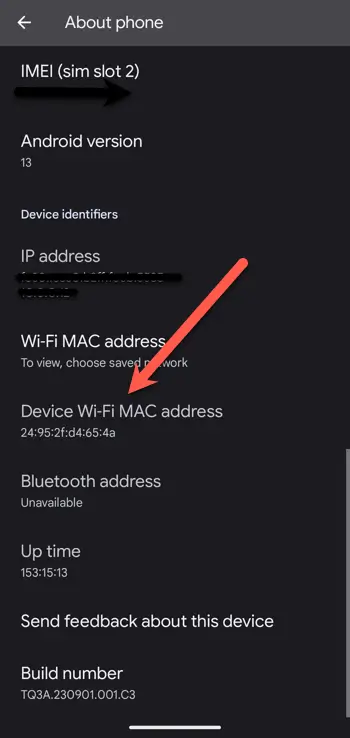
How to find your MAC on Android
To find the address on Android:
1. From the home screen, swipe up to access Search.
2. In the search box, type Settings.
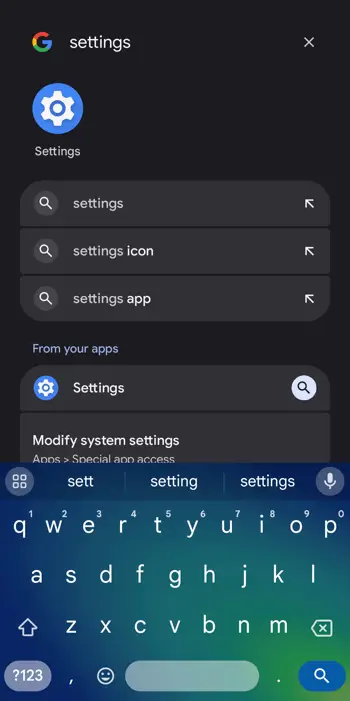
3. Scroll down and select About Phone.
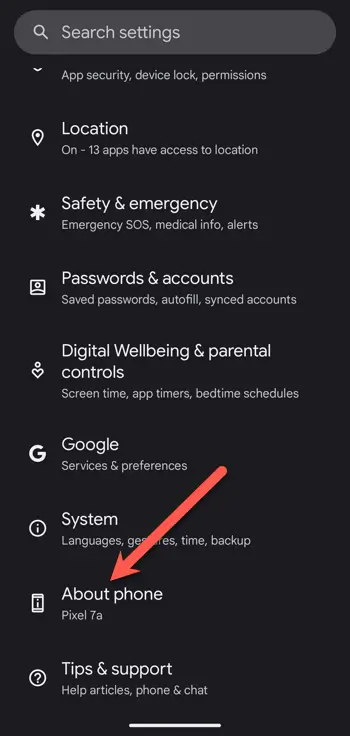
4. Scroll to the Device Identifiers section. The MAC address for your device will be listed under Device WiFi MAC Address.
Frequently asked questions
Can two devices have the same MAC address?
No, two phones or computers can't have the same MAC address. The MAC system is global, unlike the IP addressing system; therefore, no repeats are allowed.
Can I identify a device by its MAC?
Yes, you can identify a device by its MAC.
Can someone change your MAC?
While the MAC address is hard-coded onto a device's network interface controller, some drivers to allow the address to be changed.

